

Article-11
THE MIRACLE OF HUMAN BRAIN
Dr. Riya Mehta
(MPT in Neurological Conditions)
The human brain is the greatest wonderful creation of human body. Can you imagine the miracle that this tiny organ does? Yes actually this miracle is known as neuroplasticity.
What is neuroplasticity ?
It is the ability of nervous system to change its activity in response to intrinsic or extrinsic stimuli by reorganizing its structure, functions or connections. The medical world once thought that brain stops developing after childhood but neuroplasticity concept has changed this thinking.
Neuroplasticity can involve functional changes due to brain damage or structural changes due to learning. Changes can be beneficial, neutral or negative.
What is the mechanism of neuroplasticity ?
- Neuronal regeneration/ collateral sprouting
- Functional reorganization
Neuronal regeneration also includes synaptic plasticity which means ability to make experience dependent long lasting changes in strength of neuronal connections.
Functional reorganization contains three terms:
- Equipotentiality – when one area of brain is damaged the opposing side of brain would be able to sustain lost function.
- Vicariation – brain can reorganize other portions of brain to overtake functions they were not intend to.
- Diaschisis - it is concept that damage to one part of brain would cause a loss of function in another area due to some connected pathway
What is the history of neuroplasticity ?
It was first applied to behavior in 1890 by William James in The Principles of Psychology. But this theory was neglected. The first evidence of neuroplasticity came into the world by Italian anatomist Malacarne. Then in mid to later half of 20th century, following a wide range of research which showed many aspects of brain can change even in adulthood, that the term neuroplasticity came into prominence.
Which are the types of neuroplasticity ?
1. Structural
- Synaptic plasticity :- refers to change in strength of synapse
- Synaptogenesis :- formation and fitting of synapse or group of synapse into neural circuit.
- Neuronal migration :- it is the process in which neurons travel from their place of birth to final position in cortex.
- Neurogenesis :- formation of new neurons
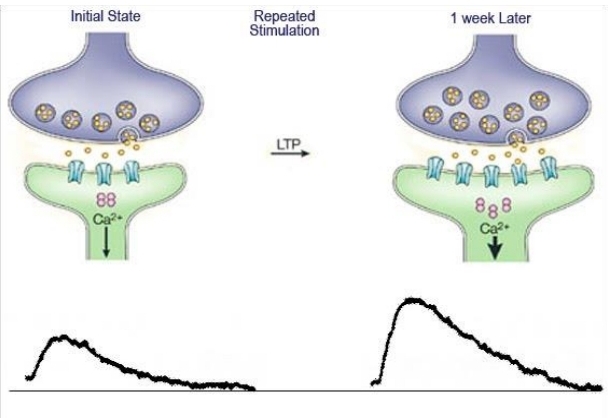
2. Functional
- It occurs at molecular level through modifications in neurotransmitter signaling, receptor levels, ion channel properties and gene expression depending upon memory and learning.
- There are permanent changes in synapse due to learning and development.
Why is neuroplasticity important ?
It allows for healing and recovery in brain injury caused by direct physical trauma or possibly a brain disease. It does so by rearranging its neural function and pathways as well as physical structure. To enhance recovery in patients there are 10 principles of neuroplasticity which can be used.
Principles of neuroplasticity :
There are 10 principles which can be used in rehabilitation to enhance neuroplasticity in patients.
-
Use it or lose it :
– Failure to use specific brain functions can lead to loss of that function. -
Use it and improve it :
– training a specific function can lead to enhancement of that function. -
Specificity :
- learning new or re-training old skill increase connections in brain. -
Repetition matters :
– Repetition of particular skill can lead to long term changes in brain. -
Intensity matters :
- Induction of plasticity requires sufficient intensity of training task. It increases number of synapses. -
Time matters :
– Earlier the onset of training better the plasticity. -
Salience matters :
- The training task should be important, relevant and have meaning to the individual. -
Age matters :
– Training induced plasticity is more in younger brains. -
Transference :
- One training experience can enhance acquisition of similar behaviors. -
Interference :
- Plasticity in terms of bad habits can interfere with learning good habits.